From retraining those displaced by automation to preventing the rise of tech monopolies, the shift into the digital age is rife with challenges. But the readiness of China's government to embrace the digital age, pursue supportive policies, and avoid excessive regulation has already placed the country at a significant advantage.
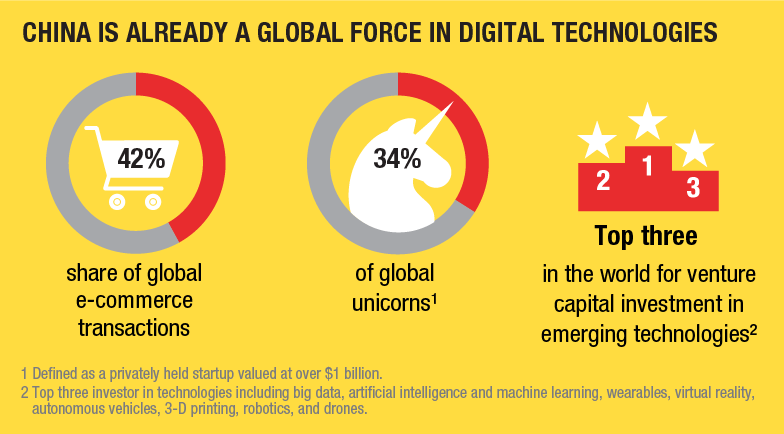
SHANGHAI – China has firmly established itself as a global leader in consumer-oriented digital technologies. It is the world’s largest e-commerce market, accounting for more than 40% of global transactions, and ranks among the top three countries for venture capital investment in autonomous vehicles, 3D printing, robotics, drones, and artificial intelligence (AI). One in three of the world’s unicorns (start-ups valued at more than $1 billion) is Chinese, and the country’s cloud providers hold the world record for computing efficiency. While China runs a trade deficit in services overall, it has lately been running a trade surplus in digital services of up to $15 billion per year.
Powering China’s impressive progress in the digital economy are Internet giants like Alibaba, Baidu, and Tencent, which are commercializing their services on a massive scale, and bringing new business models to the world. Together, these three companies have 500-900 million active monthly users in their respective sectors. Their rise has been facilitated by light – or, perhaps more accurate, late – regulation. For example, regulators put a cap on the value of online money transfers a full 11 years after Alipay introduced the service.

SHANGHAI – China has firmly established itself as a global leader in consumer-oriented digital technologies. It is the world’s largest e-commerce market, accounting for more than 40% of global transactions, and ranks among the top three countries for venture capital investment in autonomous vehicles, 3D printing, robotics, drones, and artificial intelligence (AI). One in three of the world’s unicorns (start-ups valued at more than $1 billion) is Chinese, and the country’s cloud providers hold the world record for computing efficiency. While China runs a trade deficit in services overall, it has lately been running a trade surplus in digital services of up to $15 billion per year.
Powering China’s impressive progress in the digital economy are Internet giants like Alibaba, Baidu, and Tencent, which are commercializing their services on a massive scale, and bringing new business models to the world. Together, these three companies have 500-900 million active monthly users in their respective sectors. Their rise has been facilitated by light – or, perhaps more accurate, late – regulation. For example, regulators put a cap on the value of online money transfers a full 11 years after Alipay introduced the service.